- Home Page
- Fact Tours
Our sample tour itineraries of China and China travel packages are sorted by theme and available at competitive prices, you can browse what tours are right for you for your trip to China.
Popular China Tour Packages

Custom Tour Packages to China and Ask Our Experts for Free Enquiry !
- Coach Tours
- Destinations
Beijing, the capital of China. Its art treasures and universities have long made it a center of culture and art in China.
Beijing Top Attractions
Beijing City Tours
Best China Tours with Beijing
Shanghai, the cultural and economic center of East Asia. It renowned for its historical landmarks, the extensive and growing skyline.
Shanghai Top Attractions
Shanghai City Tours
Best China Tours with Shanghai
Xi'an, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties. It is the top destination to explore the facts of Chinese history.
Xi'an Top Attractions
Xi'an City Tours
Best China Tours with Xi'an
Huangshan boasts its culture, beautiful rivers, villages and mountains. It's home to 2 UNESCO World Heritage Sites and the Mecca of photographers.
Huangshan Top Attractions
Huangshan City Tours
Best China Tours with Huangshan
Sichuan is the cradle of the Shu culture, panda, mahjong, teahouse and spicy food. The province ranks first in China by number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is called "the Heaven of Abundance".
Sichuan Top Attractions
Sichuan Tour Packages
Best China Tours with Sichuan
Yunnan, literally means the south of colorful clouds, due to its beautiful landscapes, mild climate and diverse ethnic cultures and traditions, is one of China's major tourist destinations.
Yunnan Top Attractions
Tibet, the nearest land to the sky, is known for its breathtaking landscape, splendid culture, art, buildings, and mysterious religions.
Tibet Top Attractions
Tibet Tour Packages
Best China Tours with Tibet
Explore the lost civilizations by riding a camel! Travel across the Gobi and the desert, and over the high mountains. Our Silk Road tours including different sections of the Silk Road in China.
Silk Road Top Attractions
Silk Road Tour Packages
Best China Tours with Silk Road
Guilin, an internationally-known historical and cultural city, has long been renowned for its unique karst scenery. Its vicinities are the paradise of hiking, caving, rafting, biking and countryside exploring.
Guilin Top Attractions
- China Facts
- China Hotels
- Travel Photos
Design China Tour!
Not find a wish tour? Select from A La Carte. We do the rest on your interest!
Destinations
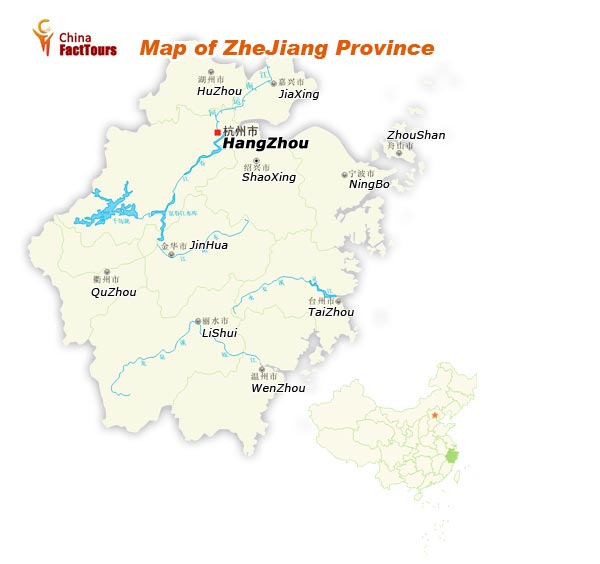
Zhejiang
Adjacent to Shanghai, Zhejiang is located in the soouthern flank of the Yangtze River Delta along the southeast coast of China, with Hangzhou as its capital city. "In heaven there is paradise; on earth there are Suzhou and Hangzhou" is a proverb known to every Chinese.
Tourist Attractions
Mt. Moganshan
Lingyin Temple
West Lake in Hangzhou
Temple of General Yue Fei
Dragon Well & Longjing Tea
Meijiawu Tea Village
Wuzhen Water Town
Hangzhou Longjing Tea Plantation
China Tea Museum
Hangzhou Southern Song Imperial Kiln Museum
Pagoda of the Six Harmonies (Liuhe Pagoda)
Traditional Chinese Medicine Museum
Zhejiang Provincial Museum
Hanghzou's fabled West Lake is probaly China's best-known beauty spot. With its willow trees, lotus blossoms in July and arched stone bridges, it confirms to every one's ideal of what Chinese scenery should look like. Many Chinese come here for sightseeing. The huge lake has four landscaped islands and the whole area is dotted with pavilions and temples. In addition to enjoying the scenery, tourists may visit silk factories (as in Suzhou) and also one of the tea plantations producing the famous Dragon Well tea. Dubbed as "Golden Sprout," it is known as the king of green tea and famous for its green color, fragrance, good taste, and beautiful shape.
Encompassing 6,400-plus km of coastlines and over 3,000 islands, it has formed a large ports. Ningbo's Beilun Port has the 3rd and 4th generation international container ternimals, 14 berths ranging in capacity from 25,000 to 200,000 tons and smooth navigable fairways for 200,000 ton ships. Its annual handling capacity ranks 2nd in China. It has established 98 sister ties with various provinces, states, cities and counties in 32 countries, including Japan, the USA, Germany, Australia, the UK, France, Italy and the Republic of Korea. It has also established business relations with more tahn 190 countries and regions all over the world.
History
Zhejiang was outside the sphere of influence of early Chinese civilization during the Shang Dynasty (sixteenth century to eleventh century BC). Instead it was populated by peoples collectively known as the Yue, such as the Dongyue and the Ouyue. Starting from the Spring and Autumn Period, a state of Yue emerged in northern Zhejiang that was heavily influenced by Chinese civilization further north, and under King Goujian of Yue it reached its zenith and was able to wipe out, in 473 BC, the state of Wu further north, a major power at the time. In 333 BC, this state was in turn conquered by the state of Chu further west; and the state of Qin in turn subjugated all the states of China under its control in 221 BC, thereby establishing a unified Chinese empire.
Throughout the Qin Dynasty (221 to 206 BC) and Han Dynasty (206 BC to 220 AD), Zhejiang was under the control of the unified Chinese state, though it was a frontier area at best, and southern Zhejiang was not under anything more than nominal control, it being still inhabited by Yue peoples with their own political and social structures. Near the end of the Han Dynasty Zhejiang was home to minor warlords Yan Baihu and Wang Lang, who fell in turn to Sun Ce and Sun Quan, who eventually established the Kingdom of Wu (222–280), one of the Three Kingdoms.
From the fourth century onwards, China began to be invaded from the north by nomadic peoples, who conquered areas of North China and established the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Northern Dynasties. As a result, massive numbers of refugees arrived from the north and poured into South China, which hosted the refugee Eastern Jin Dynasty and Southern Dynasties; this accelerated the sinicization of South China, including Zhejiang.
The Sui Dynasty reestablished unity and built the Grand Canal of China, which linked Hangzhou to the North China Plain, providing Zhejiang with a vital link to the centers of Chinese civilization. The Tang Dynasty (618–907) presided over a golden age of China. Zhejiang was, at this time, part of the Jiangnandong Circuit, and there began to appear references to its prosperity. Later on, as the Tang Dynasty disintegrated, Zhejiang constituted most of the territory of the regional kingdom of Wuyue.
The Northern Song Dynasty re-established unity in around 960. Under the Song Dynasty, the prosperity of South China began to overtake North China. After the north was lost to the Jurchens in 1127, Zhejiang had its heyday: the modern provincial capital, Hangzhou, was the capital of the Han Chinese Southern Song Dynasty which held on to South China. Renowned for its prosperity and beauty, it may have been the largest city in the world at the time. Ever since then all the way to the present day, north Zhejiang has, together with neighbouring south Jiangsu, been synonymous with luxury and opulence in Chinese culture. Mongol conquest and the establishment of the Yuan Dynasty in 1279 ended Hangzhou's political clout, though Hangzhou continued to prosper; Marco Polo visited the city, which he called "Kinsay", and called the "finest and noblest city" in the world".
The Ming Dynasty which drove out the Mongols in 1368 were the first to establish Zhejiang Province, and the borders of the province have since changed little. With the invasion of Western capitalism, Zhejiang became the most important bridge between Shanghai, the national economic center, and wealthy Southern China. Following the Doolittle Raid during world war II, most of the B-25 American crews that came down in China eventually made it to safety with the help of Chinese civilians and soldiers. The Chinese people who helped them, however, paid dearly for sheltering the Americans. The Imperial Japanese Army began the Zhejiang-Jiangxi Campaign to intimidate the Chinese from helping downed American airmen. The Japanese killed an estimated 250,000 civilians while searching for Doolittle’s men.
After the People's Republic of China took control of Mainland China in 1949, the Republic of China government based in Taiwan continued to control the Dachen Islands off the coast of Zhejiang until 1955, even establishing a rival Zhejiang provincial government there, creating a situation similar to Fujian province today. During the Cultural Revolution (1966–76), Zhejiang was in chaos and disunity, and its economy was stagnant, especially during its high tide (1966–69). These problems were intensified by an agricultural policy favoring grain production at the expense of industrial and cash crops. Mao’s self-reliance policy, and the reduction in maritime trade cut off the lifelines of the port cities of Ningbo and Wenzhou. While Mao invested heavily in railroads in interior China, no major railroads were built to improve the poor transportation conditions in South Zhejiang.Zhejiang has been less favored by the central government due to the lack of natural resources, a location vulnerable to potential flooding from the sea, and an economic base at the national average. Zhejiang, however, has long been an epicenter of capitalist development in China, and has been leading the nation in marketisation and the development of private enterprises. Northeast Zhejiang, as part of the Yangtze Delta, is flat, more developed, and industry oriented, where the earliest civilization in Zhejiang was found. South Zhejiang is mountainous and ill-suited for farming, and has traditionally been poor and underdeveloped. The economic reforms of Deng Xiaoping, however, have brought change to that region unparalleled across the rest of China. Driven by hard work, an entrepreneuring spirit, low labour costs, and an eye for the world market, south Zhejiang (especially cities such as Wenzhou and Yiwu) has become a major center of export. This, together with the traditional prosperity of north Zhejiang, has allowed Zhejiang to leapfrog over several other provinces and become one of the richer provinces of China.
Although against the traditional Confucian ideas, intellectuals in Zhejiang, such as Shi Ye of the Yongjia School, had been promoting commercial activities. Over the years, Zhejiang has developed a tradition of active commercial activities and entrepreneurship.
Geography
Zhejiang consists mostly of hills, which account for about 70% of its total area. Altitudes tend to be highest to the south and west, and the highest peak of the province, Huangyajian Peak (1921 m), is found in the southwest. Mountain ranges include the Yandang Mountains, Tianmu Mountains, Tiantai Mountains, and Mogan Mountains, which traverse the province at altitudes of about 200 to 1000 m.
Valleys and plains are found along the coastline and rivers. The north of the province is just south of the Yangtze Delta, and consists of plains around the cities of Hangzhou, Jiaxing, and Huzhou, where the Grand Canal of China enters from the northern border to end at Hangzhou; another relatively flat area is found along the Qujiang River, around the cities of Quzhou and Jinhua. Major rivers include the Qiantang River and the Oujiang River. Most rivers carve out valleys in the highlands, with plenty of rapids and other features associated with such topography. Famous lakes include the West Lake of Hangzhou and the South Lake of Jiaxing.
Climate
Zhejiang has a humid subtropical climate with four distinct seasons. Spring starts in March and is rainy and weather is changeable. Summer, from June to September is long, hot and humid. Fall is generally dry, warm and sunny. Winters are short but cold except in the far south. Average annual temperature is around 15 to 19°C, average January temperature is around 2 to 8°C, and average July temperature is around 27 to 30°C. Annual precipitation is about 1000 to 1900 mm. There is plenty of rainfall in early summer, and by late summer Zhejiang is directly threatened by typhoons forming in the Pacific.
Opera
Zhejiang is the home of Yueju, one of the most prominent forms of Chinese opera. Yueju originated in Shengzhou and is traditionally performed by actresses only, in both male and female roles. Other important opera traditions include Yongju (of Ningbo), Shaoju (of Shaoxing), Ouju (of Wenzhou), Wuju (of Jinhua), Taizhou Luantan (of Taizhou) and Zhuji Luantan (of Zhuji).
Products
Longjing tea (also called dragon well tea), originating in Hangzhou, is one of the most prestigious, if not the most prestigious Chinese tea. Hangzhou is also renowned for its silk umbrellas and folding fans.
Cuisine
Zhejiang cuisine (itself subdivided into many traditions, including Hangzhou cuisine) is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine.
Home | About Us | Partnerships | Terms & Conditions | Privacy & Security | Payment Guide | Resource Links| Sitemap
Email: contact@chinafacttours.com, Tel: +86-773-3810160, Fax: (+86) 773-3810333
Copyright © 2008-2022 China Fact Tours. All rights reserved
![]()